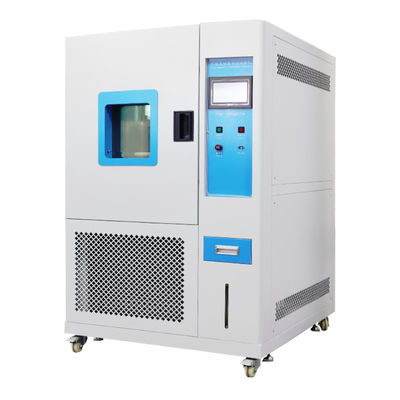
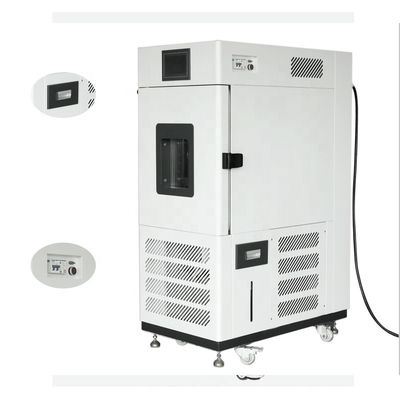
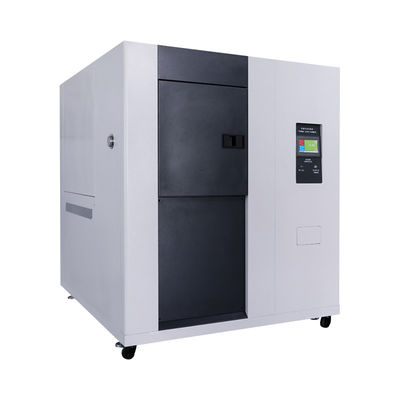
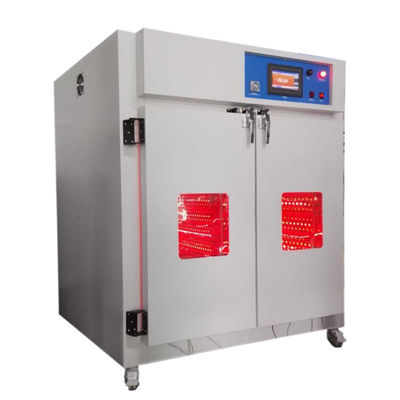
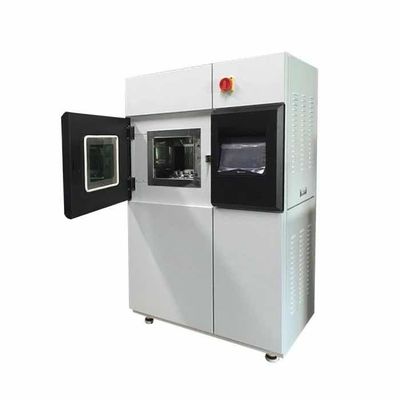
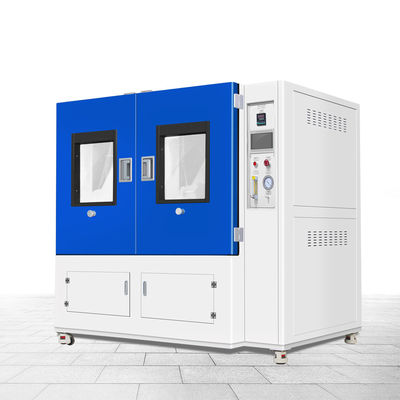
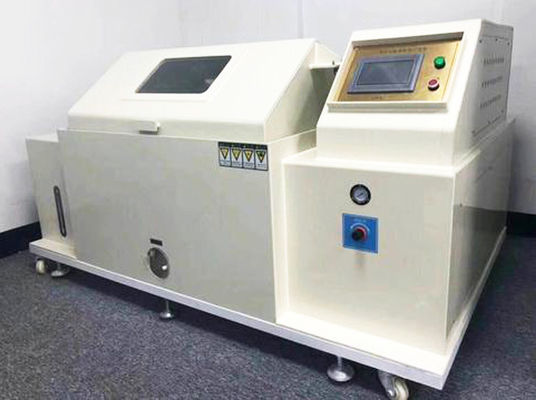
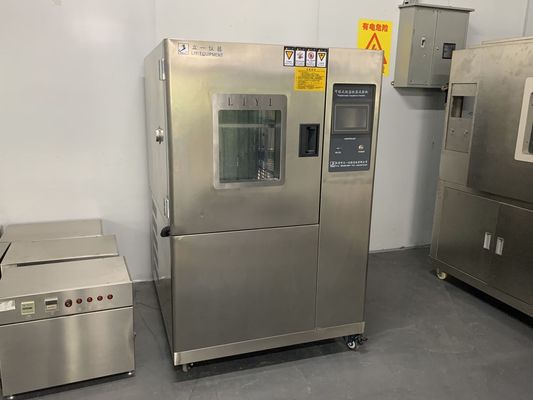
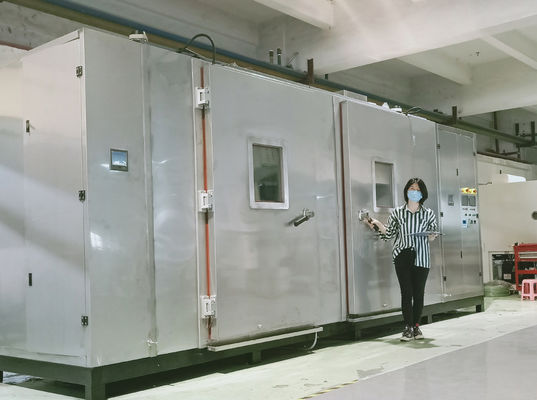
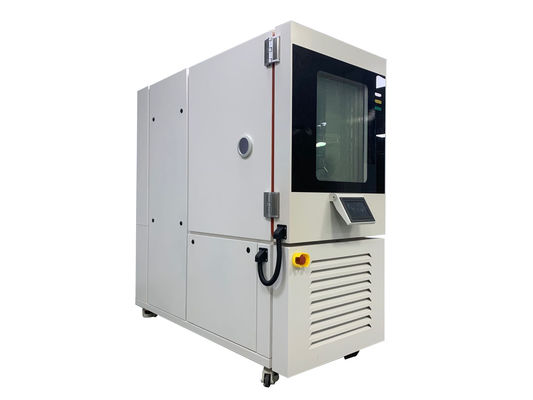
High and low temperature testing is a method used to determine the suitability of products for storage, transportation and use under high temperature climatic conditions. The severity of the test depends on the temperature of the elevated temperature and the duration of exposure. High and low temperature test is the abbreviation of high temperature test and low temperature test. The purpose of the test is to evaluate the impact of high and low temperature conditions on the performance of equipment during storage and operation.
1. Non-heat-dissipating samples and heat-dissipating samples
The test is carried out under natural air conditions. After the temperature of the test sample is stabilized, the temperature of the surface hot spot is still higher than the ambient air temperature by more than 5°C, which is called the heat dissipation test sample; the sample equal to or below 5°C is the non-heat dissipation test sample. All non-working storage and transportation tests are non-heat dissipation tests. During the test under the working state, when the temperature of the test sample is stable, the temperature rise less than 5℃ is also called the non-heat dissipation test. For example, after the type test of the electric fan, if the temperature rise of the easily accessible outer surface is not higher than 20℃, it is a heat dissipation test.
2. Temperature mutation test and temperature gradient test
When the temperature of the test box (chamber) rises or falls to the specified temperature, immediately put the sample into the test box for testing, which is called the temperature mutation test. The test in which the internal temperature gradually rises or falls to the temperature specified in the test is called the temperature gradient test.
Generally speaking, if it is known that the sudden change of temperature will not have other harmful effects on the test sample, in order to save the test time, the sudden change of temperature test should be used, otherwise the temperature gradient test should be used.
3. No forced air circulation test and forced air circulation test
In the non-heat dissipation test, forced air circulation can be used to improve the heat exchange efficiency. The higher the air circulation speed, the higher the heat exchange efficiency. Therefore, it is recommended to use the air circulation speed ≥ 2m/s when carrying out this forced test. In the heat dissipation test, a better method is to use a non-forced air circulation test. If the test requirements cannot be met by using no forced air circulation, the forced air circulation test shall be used.
Test equipment and test parameters
1. Test equipment
The high temperature test is generally carried out by placing the product in a constant temperature box or a constant temperature room. The temperature of the medium is measured at different locations with a thermometer, and the arithmetic mean is taken. However, it is required that the temperature in the box is as uniform as possible, and the product is heated by the flow of hot air, and the test sample should not be placed close to the heat source. In order to reduce the influence of radiation, the wall temperature of the test chamber should not be 3% higher than the ambient temperature.
The low temperature test is generally carried out in a low temperature box (room), and its temperature is generally obtained by artificial refrigeration. Within the effective working space of the cryostat, forced air circulation is used to maintain uniformity of cryogenic conditions.
2. Test parameters
According to different regions and usage occasions, the priority values for different temperature grades are respectively specified.
Low temperature ambient temperature: -65℃, -55"C, -45"C, -40℃, -30℃, -25℃, -15℃, -10℃, -5℃, 0℃, +5℃;
High temperature ambient temperature: +200℃, +17S℃, +155℃, +125℃, +100℃, +8S℃, +70℃, +65℃, +60℃, +55℃, +50℃, +45 ℃, +40℃, +3S℃, +30℃.
The allowable deviation range of temperature is ±2℃
After the temperature of the test sample is stabilized, the duration of the high and low temperature condition test is selected from the following data as needed:
2、16、72、95(h)
The basic requirements that the product should meet after the high and low temperature test
The product quality after high and low temperature test is generally inspected according to the requirements specified in the product technical conditions or technical agreement. For example, the impact of high temperature environment on the performance of motor products is manifested in that the resistance of the conductive material increases, resulting in changes in current, and for motors that require precision, it will also affect the accuracy. Therefore, after the high temperature test, the insulation resistance should be measured in the test box, and its value should not be lower than 5MΩ, and other properties of the motor should also be tested. Under normal circumstances, if the product can meet the following basic requirements after the temperature test, it is considered that the product meets the high and low temperature requirements.
(1) There is no damage, deformation and other defects on the surface of the product. If the surface is coated, there should be no peeling, blistering or discoloration of the coating.
(2) For plastic parts, there are no cracks, blistering and deformation on the surface.
(3) There is no aging, bonding, softening and cracking of rubber products.
(4) There is no flow phenomenon in the welding parts of product parts
(5) The product performance data and structural functions meet the technical requirements, and there should be no other defects that hinder the normal operation of the product.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail! 










